Augmented Reality is a human experience enabled by hardware and, software to visualize digital elements superimposed on a physical or real space.
AR can be considered a close relative of VR that exploits the superimposition of virtual images on the reality we are seeing at that precise moment.
The goal is to “improve” the user’s perception of reality or otherwise integrate the level of information.
What is the story of Augmented Reality?
The first application of Augmented Reality was introduced to television weather forecasts with a green screen behind the presenter.
Below is a link to a YouTube video of a BBC weather forecast from 1979:
A much more recent and significant development is Google Glass. It is an AR viewer in the form of a pair of glasses launched to the public in May 2014.
It made great strides in public education using Augmented Reality and its role in everyday use.
Experiencing a different reality
No doubt the future of accessing AR is in wearable technology like smart glasses but all you need to access an Augmented Reality app is a smartphone or tablet.
These devices have been the main driving force behind the growth of popularity in recent years. The fact that it is highly accessible as they have increased the number of AR apps those have been developed for a large number of uses.
Consumers have accepted AR with both hands as demonstrated by the unprecedented success of Pokémon Go.
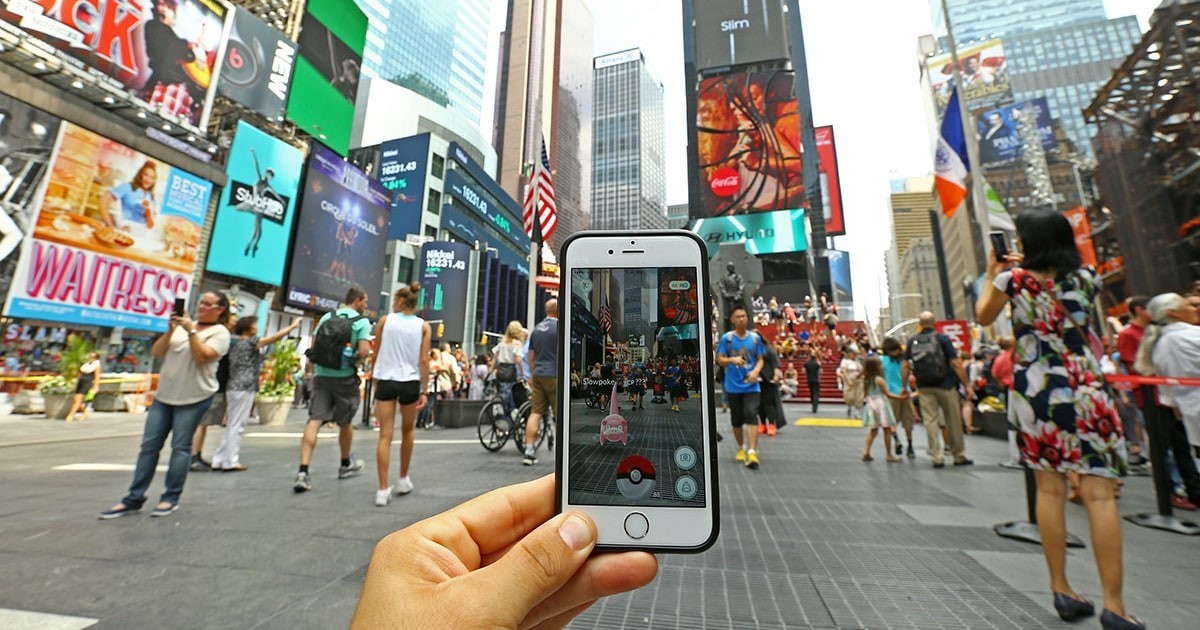

The first interesting applications for smartphones began to appear in 2009, but only today we have enough powerful hardware to allow that calculation speed to make this mix of atoms and bits usable.
In particular Google, Apple and Facebook are betting on Virtual Reality at the same time. Your smartphone is the device that enables the mass use of Augmented Reality.
It is also a real computer in everyone’s pocket equipped with increasingly powerful CPU/GPUs as well as sensors and cameras those are capable of understanding to reproduce the surrounded reality.
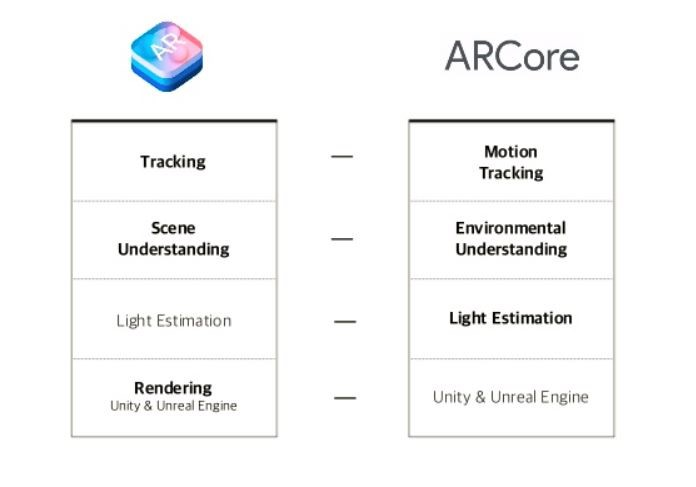
But to exploit this hardware you need a special software layer. The one by Google is called ARCore and by Apple is called ARKit. Both platforms are going to be the foundation for the most interesting applications in the most disparate sectors.
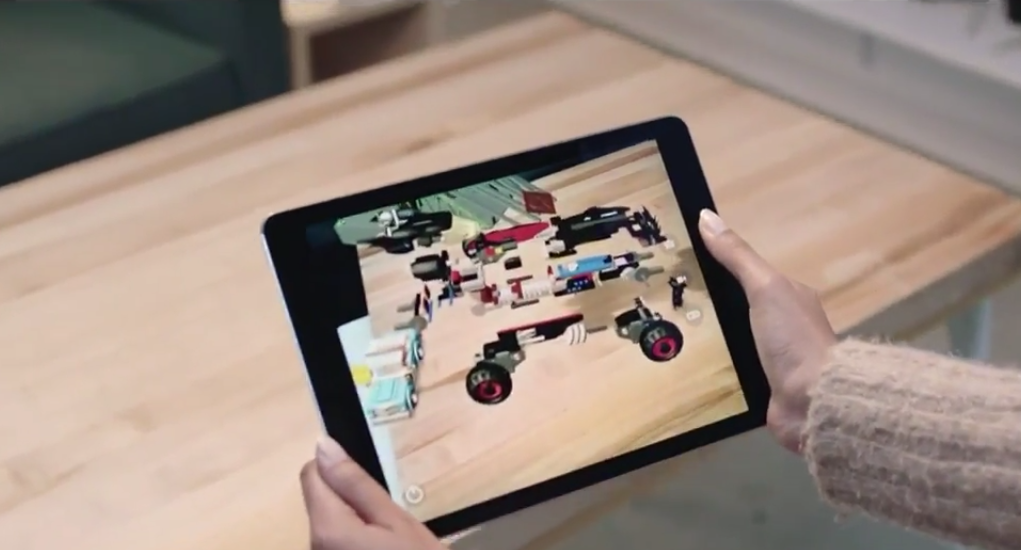

For example, augmented reality makes it possible to better evaluate a product before buying it.
Among the first experimenters there is IKEA who created Place, an app for iOS and Android that allows you to choose an object and view it three-dimensionally in the context of your home in order to simulate the ideal accommodation.
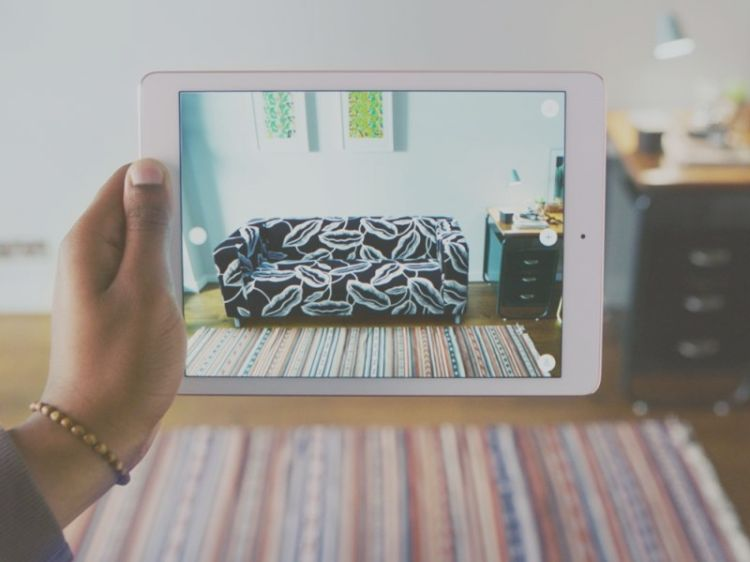

Interactive communication
Another application of Augmented Reality that starts to be explored is that linked to promotion and communication.
Snapchat and Facebook Messenger allow companies to create “three-dimensional stickers” (World Lenses and World Effects) to interact with real objects. With them users can insert the virtual characters of the two series in the surrounding world.
Also a new way to communicate a product and increase the involvement of the target audience.
eLearning
Augmented reality can also be associated with traditional e-learning in different areas of professional training like medical, pharmaceutical, scientific, industrial, commercial, hotel and many others.
An augmented reality platform allows immersive learning that is very close to a live experience.
For example, you can learn in virtual environments very similar to the real world, and interact with trainers and instructors online instantly. This can be done by avatar or with a real digital reproduction of oneself.

Gadgets
Another interesting feature of augmented reality is the possibility of creating totally immersive virtual paths. This means that just like in a video game the scenarios can have difficulty levels and motivate learners by showing them the “status” of their progress in the path.
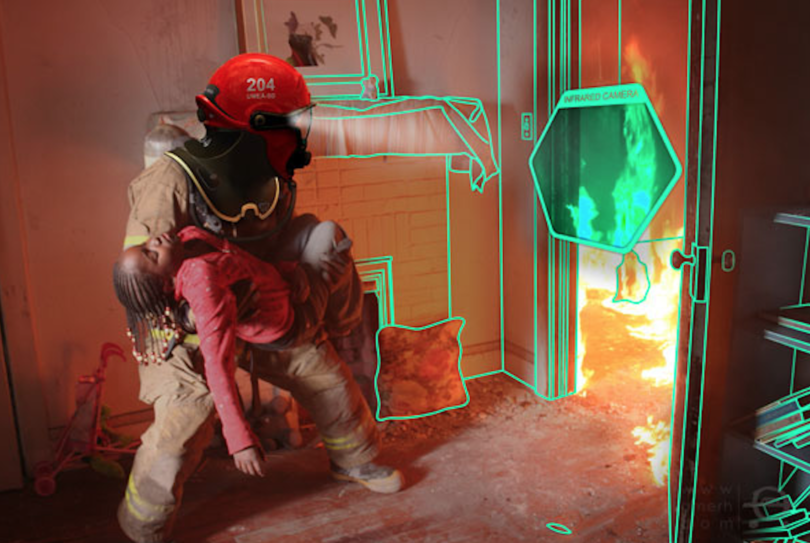
To give a concrete example, AR Firefighter helmet can train a fireman to tame a fire in the best way by simulating a path in a building on fire in which perhaps there is a human goal to be achieved.

Gaming
Businesses are exploring Augmented Reality applications in the context of social collaboration and gamification. A virtual space where learners can also solve problems.
The viewers will allow them to work together in real time and, through gloves with sensors, even interact with objects, such as 3D models and other online training tools.
This will allow students to also participate in virtual reality role-playing games that develop communication and interpersonal skills.
There are many AR applications for consumers and can be downloaded from the Apple App Store and Google Play.
There is a wide range of use cases from L’Oréal ‘Makeup Genius’ which allows users to try out various cosmetic products in virtual to an app made for Ravensburger – which allows a standard puzzle to allow an interactive experience.

To conclude, there are many applications that can show products in 3D in a B2B context as well as engineering and architecture.
This makes it ideal for sales professionals in such sectors to show how something will appear physically such as a digital creation of a building superimposed on a real lot of empty land.
AR allows brands and companies to build highly engaging and personalized experiences. You can evoke emotions that make it shareable and can easily be shared on social media.
AR is capable to offer users a better experience whether it is about viewing products, shopping, browsing a new city or engaging with advertising to access special promotions or exclusive content.






